Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is a greenhouse gas released during the combustion of carbon-containing fuels.
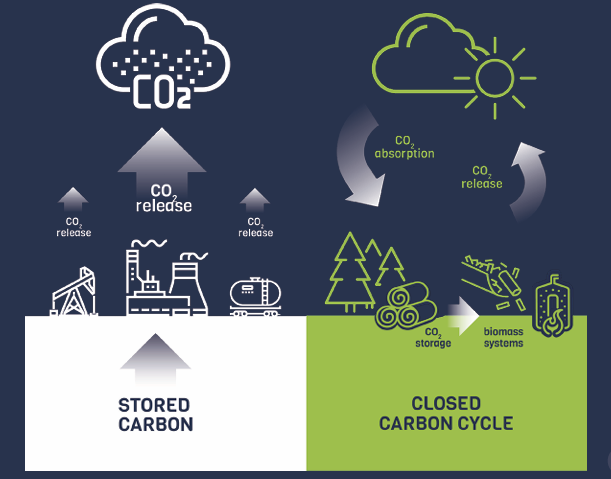
It is important to distinguish between Carbon dioxide of biogenic and fossil origin.
Biogenic carbon originates from recently living organisms, such as plants and trees, which absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. When biomass is burned or decomposes, the CO₂ released is carbon-neutral because it is part of the short-term carbon cycle.
In contrast, fossil carbon comes from ancient organic matter, such as coal, oil, or natural gas. When burned, it releases CO₂ that has been stored underground for millions of years, contributing to a net increase in atmospheric CO₂ and driving climate change.